What's Happening in Energy highlights the most interesting findings from public utility commission filings.
What's Happening in Energy highlights the most interesting findings from public utility commission filings.
Subscribe below to get these insights delivered straight to your inbox:

Editor's note: Halcyon launched its latest data product, a Large Load Tariff Tracker, this week! Read more about it here, or reach out below for a preview of the data and pricing information.
What's Happening in Energy — July 18
Powered by Halcyon
__
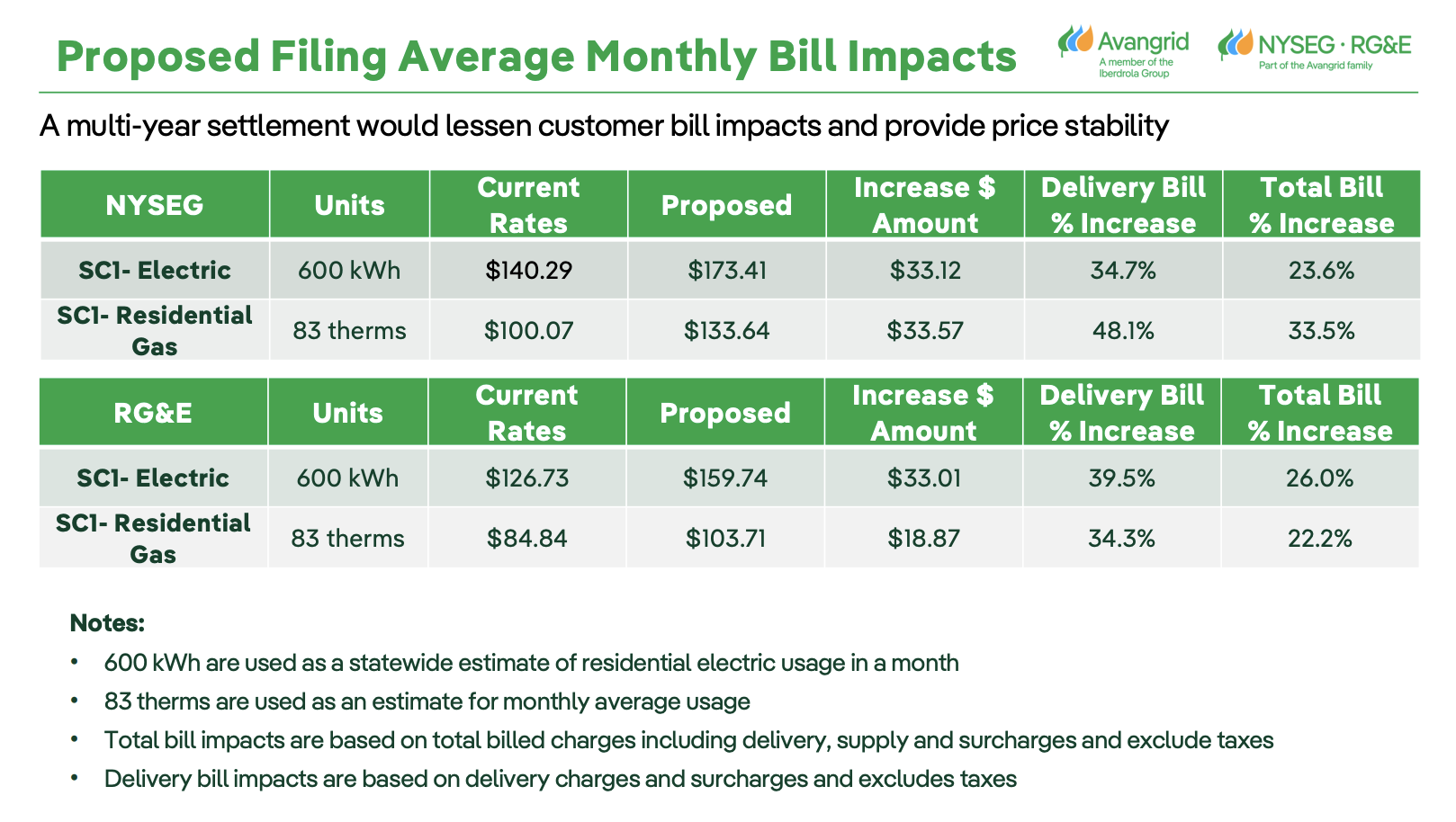
In New York, New York State Electric & Gas Corporation (NYSEG) and Rochester Gas and Electric Corporation (RG&E) filed for a rate increase with the New York Public Service Commission of roughly $850 million in the first year and an estimated 12% growth rate over five years. They included a breakdown of the rate increases by utility, first-year cost drivers, and estimated monthly bill impacts. At the highest level, NYSEG residential gas customers would experience a monthly total bill increase of 33.5%.


__
In Iowa, River City Energy is moving forward with its 500 MW solar PV facility. The company filed a Project Map with the Iowa Utilities Commission. The yellow boundaries represent the project boundaries, and the Point of Interconnection, labeled at the top connects the facility to a gen-tie line and substation that River City plans to construct.

__
In Nevada, NV Energy filed its June 2025 Distribution Reliability Report with the Public Utilities Commission of Nevada. They included data on their rolling 24-month causes of outage. Number one cause for the most outages? “Unknown.”

__
In New Mexico, the New Mexico Public Regulation Commission is considering the proposed acquisition of New Mexico Gas Company, Inc. (NMGC) by Saturn Utilities Holdco, LLC. The acquisition would involve the transfer of parent ownership of NMGC from publicly traded company, Emera Inc., to a private equity infrastructure fund, BCP Infrastructure Funds, led by Bernhard Capital Partners. The revised application included a depiction of the corporate structures both before and after acquisition.

____
In Virginia, Appalachian Power Company (APCo) has petitioned the Virginia State Corporation Commission to securitize $1.375 billion to finance distribution-related storm restoration costs incurred between January 1, 2024 and March 31, 2025, as well as its Virginia share of the undepreciated plant balances of the Amos and Mountaineer coal power plants as of December 31, 2023, plus upfront financing costs. APCo estimates that securitization will save customers $175.5 million in NPV, or $11.44 per month for a residential customer using 1000 kWh compared to recovering costs through standard rate recovery mechanisms. See detailed breakdowns of the costs below:


The utility is proposing to allocate financing costs through a “Securitized Asset Costs” (SAC) rate rider, with residential customers footing most of the bill.

The supporting analysis estimated that the majority of the savings would come from the lower estimated cost of capital for bonds (estimated at 5.25-5.75%) compared to the utility’s weighted average cost of capital in its most recent base case of 8.725% (p. 82 in the petition).

The petition included a helpful visualization of the financing structure.

__
In Virginia, the Virginia State Corporation Commission accepted Dominion’s 2024 Integrated Resource Plan (IRP) as “legally sufficient.”

However, the Commission’s acceptance came with a list of caveats and requests for Dominion’s next IRP, such as using a 20-year instead of a 15-year planning horizon, including model runs where all carbon-emitting generation is retired, and allowing its models to select for long-duration energy storage, among other things. Check out more in the filing linked below.
____
In Texas, the PUCT approved Southwestern Public Service Company’s (SPS) Transmission and Distribution System Resiliency Plan (SRP). SPS seeks to implement a comprehensive plan aimed at improving the resilience of its electric grid through distribution overhead hardening, wildfire mitigation, communication modernization, and other operational flexibility and system resiliency enhancements.
The estimated cost of the plan is $538.3 million, with the following estimated bill impacts across customer classes:

__
Also in Texas, Rita Blanca Electric Cooperative (RBEC) applied for $29.92 million in funding from the Texas Energy Fund for "Project Outage Defender.” The funding would cover resiliency upgrades, including substation automation, transformer replacement, underground distribution line installation, and the replacement of wood poles with steel. In the summary of expected benefits, RBEC cited the unique experience of their members during an outage:
“As a rural area, RBEC members experience significant negative economic impacts from frequent outages. For example, during outages, dairy farms are unable to mix feed or water their cows, which drink approximately 10 or more gallons of water per day. One of RBEC’s commercial dairy members reported that the resulting lack of milk production causes approximately $2,777 loss in sales per hour, and this amount increases after the first hour by 10%. Should a dairy cow not be milked for an extended period, her production will decrease, and she will not regain full production and will have to be replaced. That is a potential loss of $18,649.25 for a 5-hour outage in milk production alone, not counting cow replacement.”
__
PJM outlined its key sources of uncertainty in a presentation on the risks and uncertainties across gas and electric systems. Key risks include scheduling gas deliveries to generators and heightened net load ramp needs due to increased renewable energy penetration.
In its discussion of risks to gas supply, the operator explained that gas generators face increased risk in procuring gas supplies for the weekend because gas utilities and industrial companies typically schedule weekend gas deliveries on Fridays, making the weekend market relatively illiquid. This introduces risks for gas generators scheduling weekend gas flows on Friday if those scheduled deliveries do not align with the dispatch realized in PJM.


PJM also highlighted emerging uncertainty related to the increased net load ramps in the evening as solar PV generation declines. Under a scenario of 26 GW of solar PV, they project a need for almost 13 GW of ramping capability on a day like Jan 20, 2025.

__
In Hawaii, a mixed bag. Hawaii Electric Company has deferred the work associated with its authorized purchase of a 46 kV mobile substation to replace one of two existing mobile substations. In a letter to the Hawaii Public Utilities Commission, HEC says that this deferral is related to the “Company’s financial circumstances,” which is potentially associated with the August 2023 windstorm and wildfires, otherwise known as the “Event” in the filing.
On the other hand, the Hawaii Green Infrastructure Authority (HGIA) has bold goals to invest in clean energy for FY2026, as outlined in its status update of the Green Energy Money $aver (GEMS) program for low and moderate-income homeowners and renters.

.png?width=50&name=34C0AE28-DE08-4066-A0A0-4EE54E5C1C9D_1_201_a%20(1).png)

